I am doing a number of ADFS to Azure AD based authentication projects, where authentication is moved to Password Hash Sync + SSO or Pass Through Auth + SSO. Once that part of the project is complete it is time to decommission the ADFS and WAP servers. This guide is for Windows 2012 R2 installations of ADFS. There are guides for the other versions online.
This guide assumes you were using ADFS for one relying party trust, that is Office 365, and now that you have moved authentication to Azure AD you do not need to maintain your ADFS and WAP server farms.
Compile a list of server names
So first check that these conditions are true. Login to the primary node in your ADFS farm. If you don’t know which is the primary, try this on any one of them and it will tell you the primary node! Run Get-ADFSSyncProperties and you will either get back a list of properties where LastSyncFromPrimaryComputerName reads the name of the primary computer or it says PrimaryComputer.
If you don’t know all your ADFS Server Farm members then you can use tools such as found at this blog for querying AD for service account usage as ADFS is stateless and does not record the servers in the farm directly.
There is no list of the WAP servers in the farm – so you need to know this server names already, but looking in the Event Viewer on an ADFS server should show you who have connected recently in terms of WAP servers.
Get CertificateSharingContainer
On the primary ADFS server run (Get-ADFSProperties).CertificateSharingContainer. Keep a note of this DN, as you will need to delete it near the end of the installtion (after a few reboots and when it is not available any more)
Check no authentication is happening and no additional relying party trusts
Login to each ADFS box and check the event logs (Application). If any service is still using ADFS there will be logs for invalid logins. Successful logins are not recorded by default, but failures are – so if you have failures to login currently happening then something is still using ADFS and so you will not be wanting to uninstall it until you have discovered that.
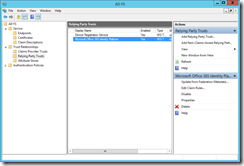
On the primary ADFS farm member open the ADFS admin console and navigate to Trust Relationships >Relying Party Trusts
If all you can see if Microsoft Office 365 Identity Platform (though it has an different name if you initially configured it years and years ago). Device Registration Service is built into ADFS, so ignore that. If you have any others, you need to work on decommissioning these before you decommission ADFS. If you have done the Azure AD authentication migration then the Office 365 Relying Party Trust will no longer be in use. Run Get-MSOLDomain from Azure AD PowerShell and check that no domain is listed as Federated. If all domains are Managed, then you can delete the relying party trust.
Uninstall Additional Connectors etc.
If you have added connectors into ADFS, for example MFA Server tools, then uninstall these first. For example if you have Microsoft MFA Server ADFS Connector or even the full MFA Server installed, then you have this and IIS to uninstall. MFA Server is removed from the control panel (there are a few different things to remove, such as MFA Mobile Web App Service, MFA User Portal etc. Remove the MFA Server piece last. IIS is removed with Remove-WindowsFeature Web-Server. If you uninstall MFA Server, remember to go and remove the servers from the Azure AD Portal > MFA > Server Status area at https://aad.portal.azure.com/ ds
Uninstall the WAP Servers
Login to each WAP server, open the Remote Access Management Console and look for published web applications. Remove any related to ADFS that are not being used any more. Look up Azure App Proxy as a replacement technology for this service. Make a note of the URL that you are removing – its very likely that this means you can remove the same name from public and private DNS as well once the service is no longer needed.
When all the published web applications are removed, uninstall WAP with the following Remove-WindowsFeature Web-Application-Proxy,CMAK,RSAT-RemoteAccess. You might not have CMAK installed, but the other two features need removing.
Reboot the box to complete the removal and then process the server for your decommissioning steps if it is not used for anything else.
Uninstall the ADFS Servers
Starting with the secondary nodes, uninstall ADFS with Remove-WindowsFeature ADFS-Federation,Windows-Internal-Database. After this run del C:\Windows\WID\data\adfs* to delete the database files that you have just uninstalled.
Remove Other Stuff
Your ADFS Service account can now be deleted, as can:
Your DNS entry, internal and external for the ADFS Service, as can:
The firewall rules for TCP 443 to WAP (from the internet), and between WAP and ADFS, as well as:
Any load balancer configuration you have. Finally, you can:
Remove the certificate entries in Active Directory for ADFS. If you have removed ALL the ADFS instances in your organization, delete the ADFS node under CN=Microsoft,CN=Program Data,DC=domain,DC=local. If you have only removed one ADFS farm and you have others, then the value you recorded at the top for the certificate is the specific tree of items that you can delete rather than deleting the entire ADFS node.
Leave a Reply